German medium anti-aircraft gun Flak 18, 36 and 37.
History, development, service, specifications, statistics, pictures, video and 3D model.
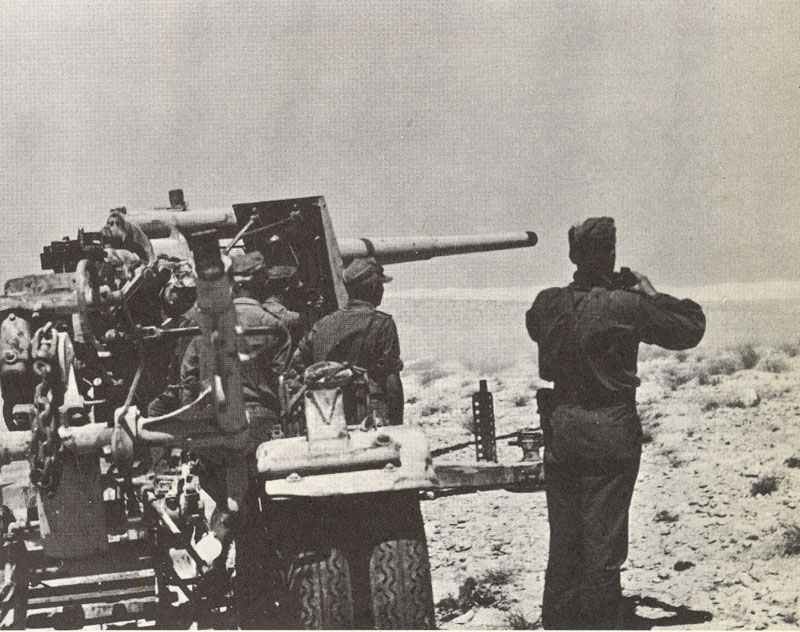

88 mm Flak
Table of Contents
88 mm gun Flak 18, 36 and 37.
Type: medium anti-aircraft gun, but often used as anti-tank or field gun.
The German 88 mm Flak gun was one of the most versatile and feared weapons of World War II. Originally designed as an anti-aircraft gun, it proved to be highly effective in multiple roles, including as an anti-tank weapon.
Overview
The 88 mm Flak (Flugabwehrkanone, meaning anti-aircraft gun) was developed in the 1920s and early 1930s, with the FlaK 18 series being developed in secrecy by Germans in Sweden to circumvent the restrictions imposed by the Treaty of Versailles. The gun evolved through several variants, including the FlaK 18, FlaK 36, and FlaK 37.
Key features of the 88 mm Flak included:
Versatility: It was a multipurpose gun capable of engaging both air and ground targets effectively.
High velocity: The gun could fire 17-pound shells at high velocities, making it deadly accurate against aircraft and armored vehicles.
Effective range: With an effective range exceeding 26,000 feet, it was a formidable anti-aircraft weapon.
Large crew: The gun required a crew of 11 men to operate efficiently, including a commander, gun operators, fuze setters, and ammunition handlers.
The 88 mm Flak gained notoriety during the war for its effectiveness against Allied tanks, especially in the North African campaign. Its high-velocity rounds could penetrate the armor of most Allied tanks at long ranges, making it a feared opponent on the battlefield.
Throughout the war, the 88 mm Flak continued to serve in its original anti-aircraft role while also proving invaluable as an anti-tank gun and even in an indirect fire support role. Its versatility and effectiveness made it one of the most iconic weapons of World War II.
History

The terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles set rigid regulations about what artillery manufacturing might be accomplished in Germany, therefore the biggest German armaments firm, Krupp of Essen, dispatched a group to Sweden to continue development and research away from enforced limitations.
Dealing with Bofors AA guns the Krupps crew worked in the beginning on a 75-mm (2.95-in) anti-aircraft weapon making use of hidden German military finances, however the Wehrmacht wasn’t especially pleased with the outcome and requested something heavier. The ‘Swedish’ Krupp team consequently created a brand new and superior 88-mm (3.465-in) gun that by 1933 was in series production at Essen as the Nazis came to power.
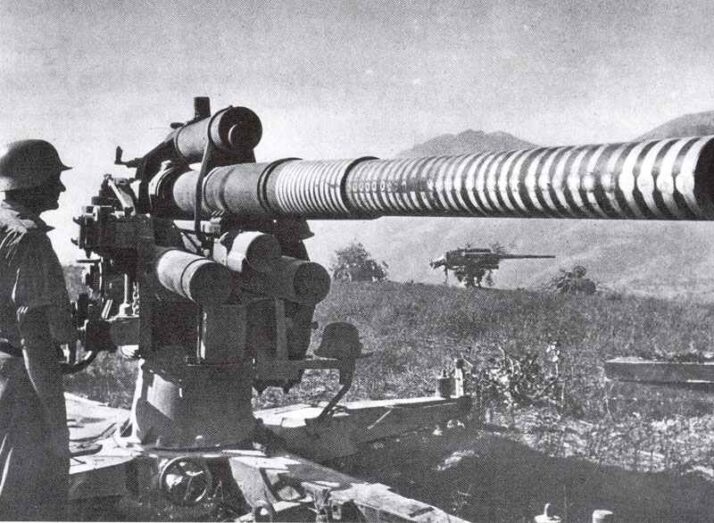
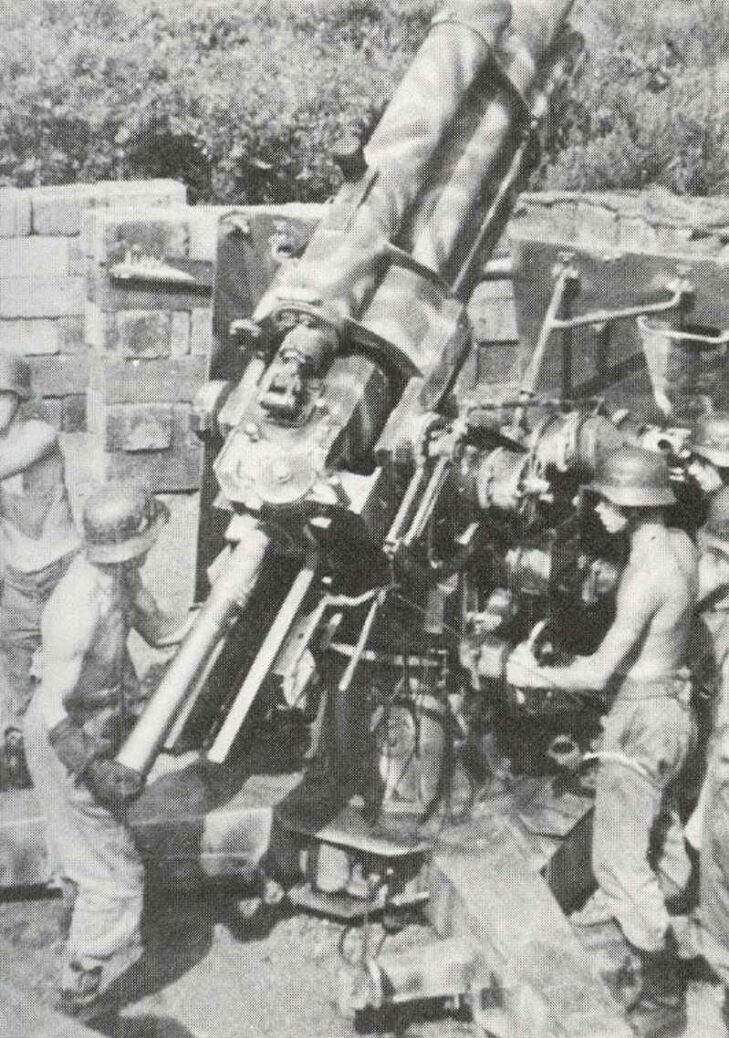
This new gun was the 8.8-cm Flak 18 (Flak standing for Fliegerabwehrkanone, or anti-aircraft gun), and it was an instantaneous success. It was a long-barreled gun mounted on a pivoted cruciform carriage, which was therefore carried on the move by dual axles that permitted the weapon to be quickly put into the firing position. The Flak 18 were built with a one-piece gun barrel but was later supplemented by a better model, the 88 mm Flak 36, which had a multisection gun barrel on which just the worn part closest the chamber must be replaced after extensive shooting.
Then arrived the 88 mm Flak 37, which was a Flak 36 having a modified system of fire-control information transmission more fitted to stationary use than field use. In reality, the 3 versions were exchangeable to a large degree, and it wasn’t uncommon to find out a Flak 18 barrel on a Flak 37 carriage. Numerous modifications had been introduced to the guns after they were operating, along with a modified twin-axle carriage design, and the 88 mm Flak line was modified to be persisted a number of self-propelled mountings, together with railway flat cars.

The 88 mm Flak series became one of the most famous weapons in the entire Wehrmacht, for it continued to be as popular as an anti-tank gun as it was as an anti-aircraft weapon: after the gun’s ‘blooding’ in Spain during the Civil War and once more in France in 1940, it was found out that the high muzzle velocity in addition to an effective and heavy projectile created the gun perfect as a ‘tank killer’. This became very evident at the time of the first North African battles against British Matilda tanks and later on Russian Front campaigns against Russian T-34 and KV heavy tank, however the 88 mm Flak series was actually exorbitant and ponderous for the anti-tank role and had to depend on its fire range and hitting power instead of concealment in action.
As anti-aircraft weapons the 88 mm Flak line was the anchor of the German field armies and of the defense of the Reich under Luftwaffe control. The type was never replaced by later versions as had been intended, and in August 1944 there have been 10,704 of all 3 versions operating. Manufacturing was carried out at a number of centers, and a wide variety of ammunition was manufactured for this weaponry, along with a large percentage of armor-piercing.
By the end of the WW2 models for stationary emplacement just were being manufactured, but at that time the 88 gun series had been utilized on self-propelled vehicles, railway mountings, coastal defense places, light shipping and in a number of trial varieties.
The 88 guns had been also used by the Italian army, as well as for some time at the end of 1944 the weapon was even used operationally by the US Army along the German borders when its own supply lines became overextended.
Numerous were used by a number of armies post-war, as well as the Yugoslav army employed the Eighty-eight gun as a coastal gun before the Civil war.
Users: Germany, Italy.

Animated 3D model of 88 mm Flak 36
Specifications for 88 mm gun Flak 18, 36, 37
Specification:
88 mm gun Flak 18, 36, 37 | specification |
|---|---|
Type | medium anti-aircraft gun, field gun and heavy anti-tank gun |
Crew | 7-10 |
Length | 25 ft 0 in |
Width | 7 ft 6.75 in |
Height | 7 ft 11.2 in |
Weight | travelling 15,126 lb; firing 11,354 lb |
Calibre | 88 mm (3.465 in) |
Length of barrel | 16 ft 2.1 in |
Length of rifling | 13 ft 6.4 in |
Traverse | 360° |
Elevation | -3° to +85° |
Muzzle velocity | 2,690 ft / sec |
Firing range | up to 26,245 ft as anti-aircraft gun; 26,250 ft as field gun |
Shell weight | Anti-Aircraft shell 19.8 lb; Anti-Tank shell 22.5 lb ; High-explosive 20.34 lb |
Practical rate of fire | 15 rounds / min. |
Penetration mm at 30° armor plates:
Range | Penetration |
|---|---|
100 meters | 127 mm |
500 meters | 117 mm |
1,000 meters | 106 mm |
!,500 meters | 97 mm |
2,000 meters | 88 mm |
Production:
88 mm gun Flak 18, 36, 37 | figures |
|---|---|
Production | Flak 17 since 1933 , 1936 replaced by Flak 36. Flak 37 in 1937. Produced until the VE-day (May 1945) |
Price per unit | 8.8-cm Pak 43 L/71: RM 26,000 = c.$5,780 = c.£1,450 |
Total production figure (all) | more than 12,000 |
Video from 88 mm Flak
88 mm gun Flak 36 firing.
References and literature
The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II (Chris Bishop)
Die Geschichte der Artillerie (John Batchelor, Ian Hogg)
Artillery in Colour 1920-1963 (Ian Hogg)
Luftwaffe Handbook (Dr Alfred Price)

















Fantastic information. What was the length of the gun and wheels when being transported?? With and without pull-tongue?