Soviet Light Infantry Tank of the Second World War.
History, development, service, specifications, statistics, pictures, and 3D model.
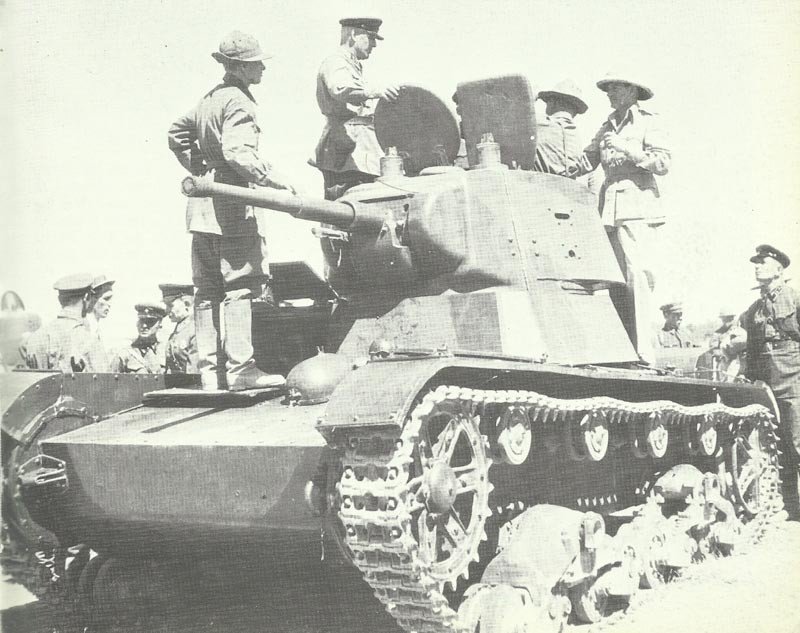

Soviet light tank T-26
Table of Contents
T-26
Type: Light tank.
The T-26 light tank was the backbone of the Soviet armored forces throughout the 1930s and early years of World War II. Developed from the British Vickers 6-Ton design, this tank became the most numerous armored vehicle in the Red Army before 1941. The T-26 was so widely produced that it formed the majority of Soviet tank forces at the time of the German invasion in June 1941, making it a crucial part of Soviet military history.
These versatile machines saw combat in numerous conflicts of the interwar period beyond Soviet borders. The cylindrical-turreted models that appeared in 1936-1937 featured searchlights for night operations, showing how the design evolved to meet battlefield needs. Various models existed, including captured variants that were repurposed by enemy forces.
Though eventually outclassed by more modern tanks as World War II progressed, the T-26’s legacy remains significant. Its widespread use and production numbers tell an important story about Soviet industrial capacity and military doctrine during a pivotal period of history. The few surviving examples in museums provide rare glimpses into this important chapter of tank development.
History
Like many other Russian tanks in the early thirties of the last century, also the T-26 was developed from a British model, which had been bought by Vickers-Armstrong. In this case, it was the 6-t-tank with two turrets, which formed the initial model.
The Russians developed from it a light infantry support tank to replace the obsolete MS. It was produced during the entire period of 1931-1940 in large series. Overall, more than 12,000 units were produced in a variety of models.
In 1930 a team of engineers of the test department (OKMO) of the Bolshevik works in Leningrad, which was headed by N W Barikow and S A Ginzbury, built 20 pre-production vehicles with the label TMM-1 and TMM-2. In a comparison test against Russian models (T-19 and T-20) they had been approved by the Revolutionary Defense Council of the Red Army on February 13, 1931. After minor changes by the engineer Sigelja it was ready for production as the T-26. Apart from a few small changes in shape at the front of the hull and on the two independent machine-gun turrets, the production vehicle corresponded completely to the British original.

In the following year, the mass production in different plants was started, including the Kirov factory in Leningrad. In the first series the turrets lay side by side and could be equipped with a variety of weapons.
The command tank T-26TU was equipped with radios. The antenna was a railing around the turret. It was intended to make a model with only one turret for the army, which was equipped with a new long-barrel 37 mm gun. However, from this model only a small series was built, because it was decided to use a single turret model with a larger turret. The mass production of this model was started in 1933. The first vehicles were armed with the new 37-mm gun, but later got the tank a newly constructed 45-mm gun.
In 1938 the Far East army reported, that the riveted T-26’s were no match for the Japanese firepower. Therefore, a new welded version, the T-26S, was designed. Some older versions of the T-26 received this turret also. Before the Russian campaign in 1941 the T-26 has already been used against the Japanese in Manchuria, in Spain and in the Russo-Finnish War.
During his service in the Russian army the T-26 has been changed on several occasions and also formed the basis of many specialist vehicles. Among them, for example, self-propelled guns, flame thrower tank, armored vehicle launched bridges, nebulization tanks, artillery tractors, remote-controlled explosive tanks and many others.
User: Russia, Spain, China, Turkey (captured specimens were used also by the Finnish, German, Romanian and Hungarian armies).

Design and Development
The T-26 tank evolved significantly throughout the 1930s, becoming the backbone of Soviet armored forces. Its design incorporated foreign influences while adapting to Soviet military requirements, eventually spawning over 50 variants.
Origins and Influences
The T-26 originated as a licensed version of the British Vickers 6-Ton tank. In 1930, the Soviet Union purchased 15 Vickers tanks along with production rights, recognizing the design’s potential for their rapidly modernizing military. Soviet engineers made several modifications to suit their needs, including improved transmission and suspension systems.
The initial twin-turret configuration mirrored the Vickers design, featuring two machine gun turrets. However, by 1933, Soviet designers shifted to a single-turret variant that could accommodate larger guns. This modification proved crucial for the tank’s longevity and adaptability.
The T-26 production was centered at Factory No. 174 in Leningrad, where manufacturing techniques evolved from largely manual methods to more efficient assembly line processes.
Armament and Armor
The T-26’s armament varied by model but showed clear progression toward increased firepower. Early twin-turret models carried only 7.62mm machine guns, limiting their effectiveness against other armored vehicles.
Later single-turret versions featured:
- 45mm Model 1932/1934 main gun
- 7.62mm DT machine gun (coaxial)
- Optional rear machine gun on some models
The 45mm gun provided adequate anti-tank capability for early 1930s combat conditions. Some specialized variants featured flamethrowers or larger caliber weapons for specific roles.
Armor protection remained a weakness throughout the T-26’s service life. Early models had only 15mm of armor at maximum, later increased to 25mm on frontal plates. This proved insufficient against German anti-tank weapons during World War II engagements on the Leningrad Front and elsewhere.
Production Variants

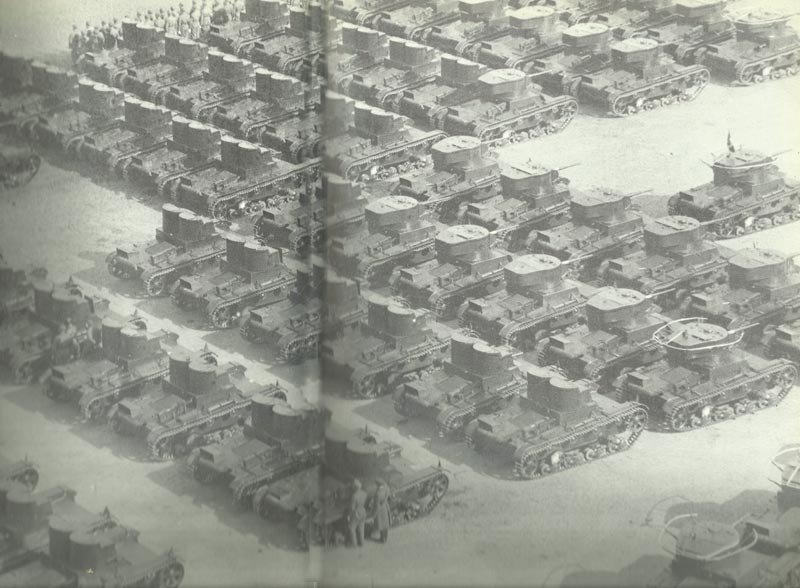
The T-26 chassis proved remarkably versatile, supporting over 50 different modifications and experimental designs. Major production variants included:
- T-26 Model 1931: Twin-turret configuration with machine guns
- T-26 Model 1933: Single turret with 45mm gun
- OT-26/OT-130: Flamethrower tanks for infantry support
- ST-26: Bridge-laying engineering vehicle
- SU-5: Self-propelled gun platforms
Specialized variants included artillery tractors, radio-controlled tanks for dangerous missions, and command vehicles. The Soviets manufactured approximately 12,000 T-26 tanks and variants from 1931 to 1941, making it the most produced tank worldwide during the 1930s.
Production quality varied throughout its run, with later models showing improvements in welding techniques and internal layouts. Despite its eventual obsolescence, the T-26 platform demonstrated remarkable adaptability.
Operational History
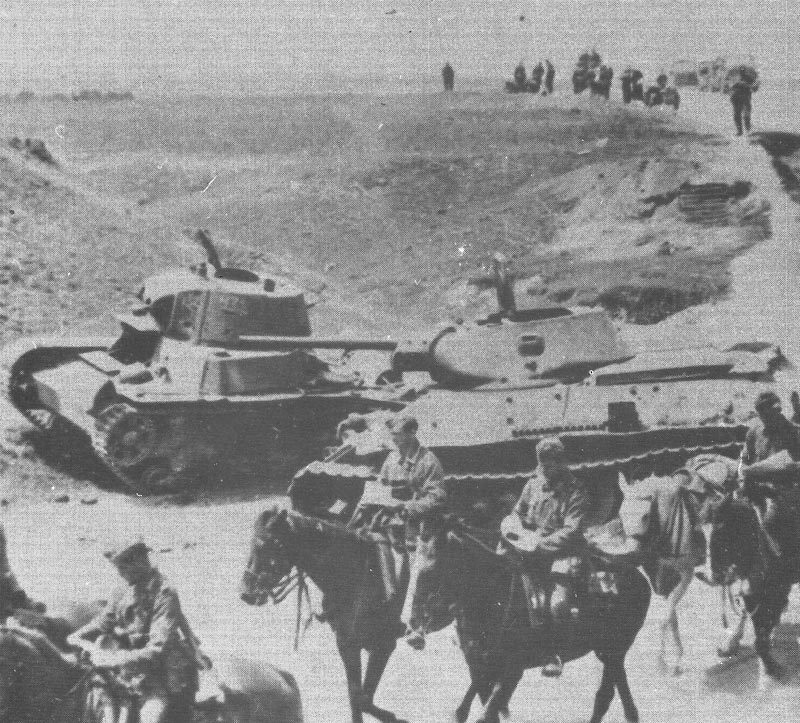

The T-26 tank served extensively from the 1930s through World War II, becoming one of the most widely deployed Soviet tanks of its era. It saw action in numerous conflicts across multiple continents and was operated by several countries beyond the Soviet Union.
Early Deployments
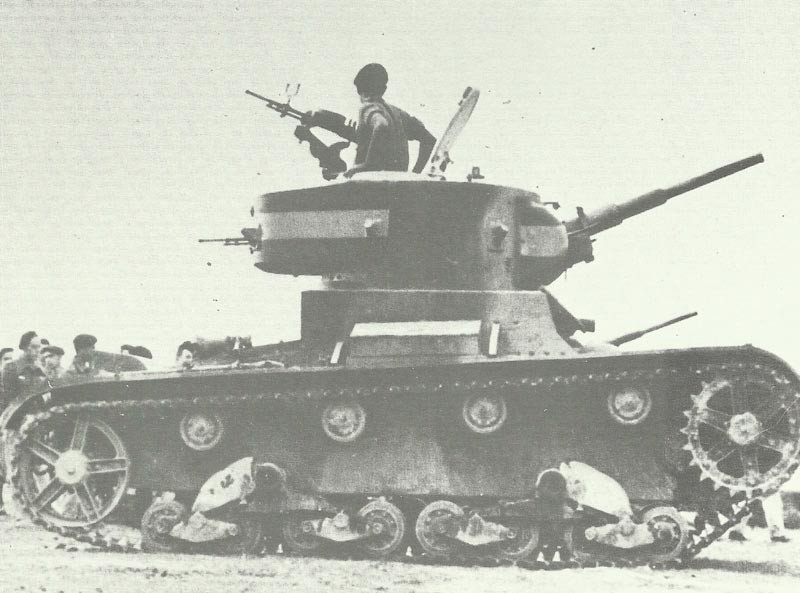

The T-26 received its baptism by fire during the Spanish Civil War (1936-1939). The Soviet Union supplied approximately 281 T-26 tanks to the Republican forces, where they proved superior to the German and Italian tanks deployed by Franco’s Nationalists.
These combat experiences provided valuable lessons for Soviet tank doctrine. The T-26 also saw action in the Soviet-Japanese border conflicts at Lake Khasan (1938) and Khalkhin Gol (1939), where they faced Japanese forces.
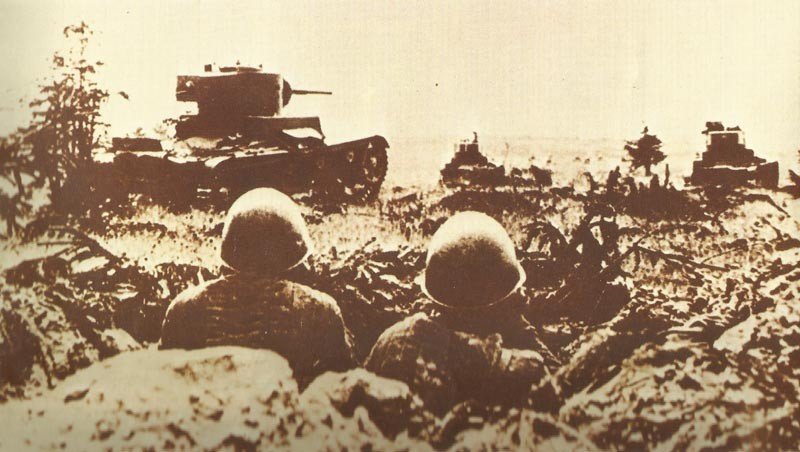

During the Winter War against Finland (1939-1940), the T-26 faced significant challenges. Finnish troops developed effective anti-tank tactics using Molotov cocktails and satchel charges. The harsh winter conditions and difficult terrain exposed vulnerabilities in the T-26’s design.
World War II Engagements
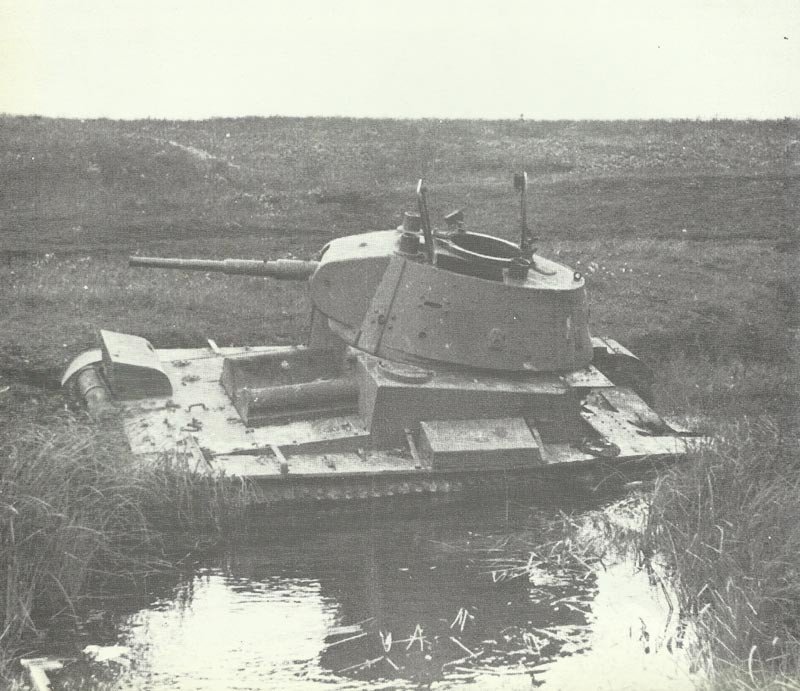

When Germany invaded the Soviet Union in 1941, the T-26 constituted about 41% of the Red Army’s tank force. Despite their numerical advantage, many T-26 tanks were lost during the initial German offensive due to mechanical failures, fuel shortages, and superior German tactics.
On the Eastern Front, the T-26’s thin armor proved inadequate against German anti-tank weapons and tanks. The 45mm gun, while effective earlier, couldn’t penetrate the armor of newer German tanks like the Panzer IV.
By 1942, the T-26 was largely replaced by the more advanced T-34 medium tank. However, remaining T-26 tanks continued to serve in secondary roles as support tanks for infantry units and in less contested sectors of the front.
Post-War Service and Foreign Use
After World War II, surviving T-26 tanks were gradually phased out of Soviet service but remained operational in other countries. China received numerous T-26 tanks and used them during their civil war and early years of the People’s Republic.
Finland captured and repurposed many T-26 tanks during the Winter War and Continuation War, keeping some in service until the 1960s. Spain maintained their Civil War-era T-26 tanks until the 1950s.
Turkey, Afghanistan, and Mongolia also operated the T-26. Some tanks survived as monuments or museum exhibits, preserving the legacy of this historically significant Soviet light tank that influenced early tank development worldwide.
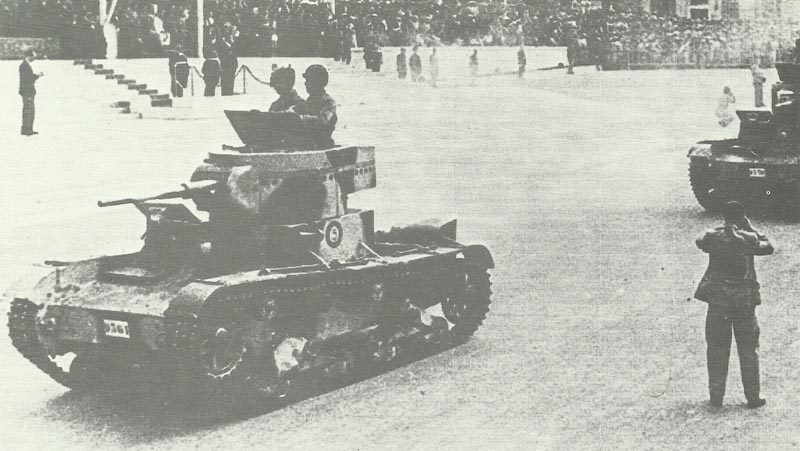

Technical Specifications
The T-26 light tank featured modest but effective specifications for its era, balancing firepower with mobility despite its limited armor protection. Its technical design reflected Soviet priorities for mass production and battlefield versatility.
Dimensions and Mobility
The T-26 measured 4.55 meters in length, 2.31 meters in width, and stood 2.30 meters tall (approximately 14ft 11in x 7ft 7in x 7ft 7in). This compact size made it suitable for various combat scenarios.
The tank had a battle-ready weight of 9.6 tons, allowing for reasonable maneuverability.
Power came from a 4-cylinder air-cooled petrol engine producing 90-91 hp (66.9-67 kW) at 2100 rpm with maximum torque of 343 Nm. This engine was a Soviet copy of the Armstrong design.
The T-26 achieved speeds of 31 km/h on roads but slowed to 16-22 km/h when traveling off-road. This modest speed was acceptable for infantry support operations.
The tank required a crew of three: commander, gunner, and driver.
Armament Details
The primary armament of the T-26 was a 45 mm cannon that delivered impressive firepower for a light tank. This gun could effectively penetrate enemy armor at its battle rating.
The weapon system utilized APHE (Armor-Piercing High-Explosive) ammunition, making it particularly devastating against lightly armored vehicles.
Most T-26 variants also featured machine guns for infantry suppression and defense against soft targets. These secondary weapons complemented the main gun.
The tank’s thin armor was its main weakness, offering minimal protection against enemy fire. However, this limitation was balanced by its relatively good firepower-to-weight ratio.
Later models received incremental improvements to both armament and protection while maintaining the basic design philosophy.
Animated 3D model T-26S:
Specifications for T-26S
Specifications:
T-26S | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | Light tank |
Engine | air-cooled 4-cylinder gasoline engine with 90 hp at 2,200 rev/min |
Gearbox | ? |
Crew | 3 |
Turret crew | 2 |
Length | 4.88 meters |
Width | 3.41 meters |
Height | 2.41 meters |
Weight | 9.4 tons |
Ground pressure | c. 0.72 kg/cm² |
Power to weight ratio | c. 9.6 PS/t |
Maximum speed | 30 km/hr |
Cross-country speed | ? |
Fuel consumption per 100 Kilometers | 130 liters on road; 195 liters cross-country |
Fuel | 292 liters |
Road range | 225 km |
Cross-country radius | 150 km |
Vertical obstacle | 0.79 meters |
Trench crossing | 1.90 meters |
Fording depth | ? |
Turning circle | ? |
Climbing power | 40° |
Armor:
T-26S | mm | angle |
|---|---|---|
Details unknown | 12-37 mm | ? |
Armament and Equipment:
T-26S | Specification |
|---|---|
Main armament | 45 mm Model 38 |
Rounds | 165 |
Traverse | 360° |
Elevation | ? |
Muzzle velocity BR-240 (HE) | 760 m/s |
Muzzle velocity BR-240P (DS) | 1,070 m/s |
Muzzle velocity O-240 (HE) | 750 m/s |
Shell weight BR-240 | 1.4 kg |
Shell weight BR-240P | 0.85 kg |
Shell weight O-240 | 2.1 kg |
Maximum firing range | ? |
Secondary armament | 1 x DT MG |
Radio | only for command tanks |
Telescopic sight | ? |
Penetration mm at 0° armor plates of the gun:
Range | BR-240 | BR-240P |
|---|---|---|
100 m | ? | ? |
500 m | 42 mm | 80 mm |
1.000 m | 38 mm | 50 mm |
1.500 m | - | - |
2.000 m | - | - |
Production:
T-26 | figures |
|---|---|
Production | 1932-1940 (special versions until 1941, T-26S since 1937-38) |
Service delivery | 1933 |
Price per unit | ? |
Total production figure | c. 12,000 |
Service statistics of all T-26 variants:
Year | Available | Production | Losses |
|---|---|---|---|
before 1940 | ? | c.10,500 ? | |
1940 | ? | 1,549 | ? |
1941 | c.11,000 (June) (only some special versions) | ? | |
1942 | ? | - | ? |
1943 | ? | - | ? |
1944 | ? | - | ? |
1945 | (out of service end 1945) | - | ? |
Total | - | c.12,000 ? |
Tactical Role and Doctrine
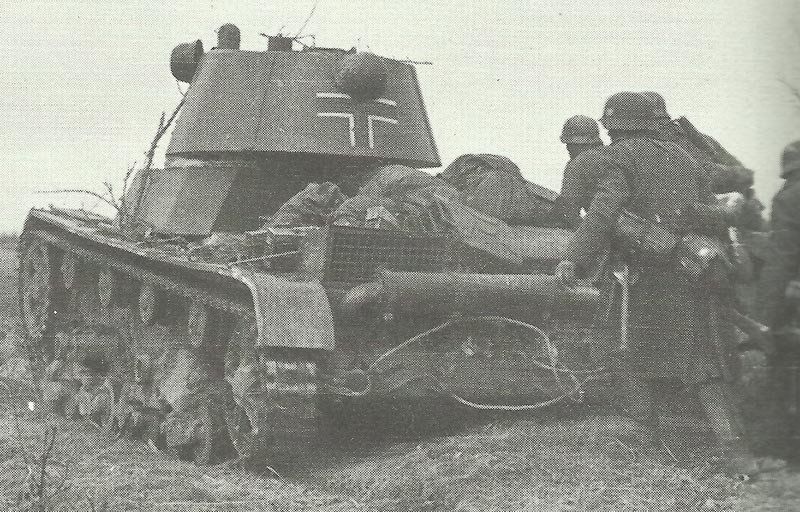

The T-26 light tank served as the backbone of Soviet armored forces in the 1930s and early 1940s. Its tactical employment evolved through several doctrinal changes and combat experiences that shaped how the Red Army utilized these vehicles on the battlefield.
Support Roles and Limitations
The T-26 primarily functioned as an infantry support tank within the Red Army. In tank brigades, T-26s operated alongside motorized infantry battalions, with their main purpose being direct fire support for advancing troops. These tanks excelled at eliminating enemy machine gun nests and light fortifications.
The tank’s relatively thin armor (maximum 25mm) made it vulnerable to anti-tank weapons, limiting its effectiveness in frontal assaults against prepared positions. By 1941, the T-26 was often deployed in small groups of 2-3 vehicles working closely with infantry units.
During the German invasion, many T-26s were lost due to mechanical breakdowns rather than enemy fire. Their limited range (about 170km) and reliability issues hampered their strategic mobility.
Comparison with Contemporaries
The T-26 compared favorably to other light tanks of its era when first introduced. It offered superior firepower to German Panzer Is and early Panzer IIs with its 45mm main gun. However, by 1941, it had fallen behind contemporary designs.
Unlike the BT series light tanks, which emphasized speed and maneuverability, the T-26 prioritized armor protection and infantry support capabilities. The BT tanks could reach speeds of 70 km/h on roads, while the T-26 managed only 31 km/h.
The T-34, which began replacing both T-26 and BT tanks from 1940 onward, represented a significant improvement in all categories:
Feature |
T-26 |
T-34 (1941) |
|---|---|---|
Main Gun |
45mm |
76.2mm |
Armor |
15-25mm |
45-60mm |
Speed |
31 km/h |
54 km/h |
By 1942, the T-26 was largely relegated to training roles as more modern tanks took over frontline duties.
Modifications and Field Upgrades
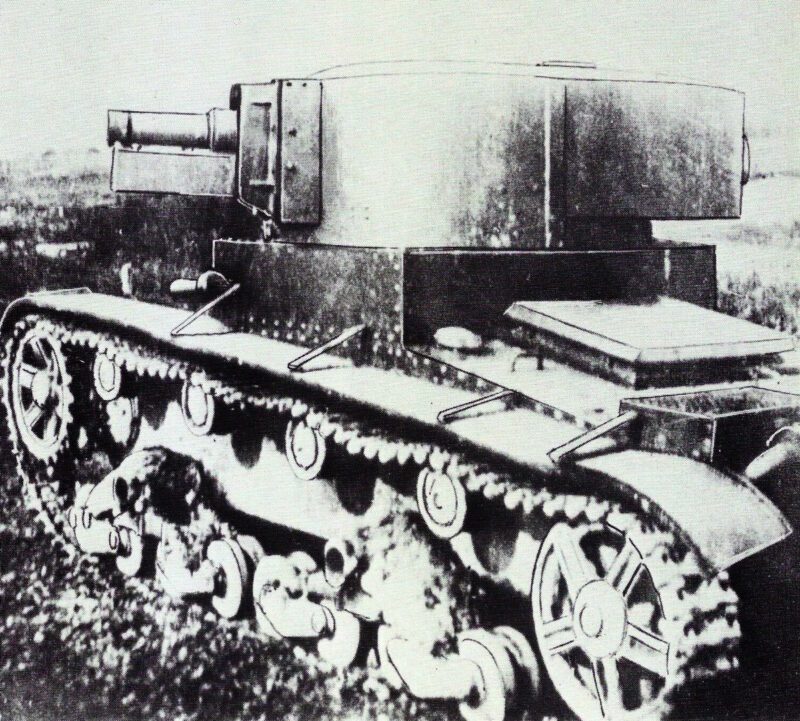
The T-26 tank platform proved incredibly versatile, with over 50 different modifications developed in the USSR during the 1930s. These ranged from factory upgrades to battlefield adaptations made by necessity during combat operations.
Self-Propelled Gun Conversions
The T-26 chassis served as an excellent base for self-propelled gun variants. Soviet engineers recognized the platform’s potential for mounting larger weapons while maintaining good mobility. The lightweight chassis (6-7 tons) could be adapted to carry different gun systems with vertical ranges from -5 to 30 degrees.
Most self-propelled variants maintained the original T-26’s speed capability of 30-35 kph, though the added weight of larger guns sometimes reduced this slightly. The standard 10mm armor protection was typically preserved in these conversions to maintain mobility advantages.
Some variants featured completely redesigned superstructures to accommodate specialized artillery pieces. These conversions carried approximately 100 shells for their main armament, balancing firepower with practical ammunition storage.
Field Modifications
During wartime, T-26 tanks frequently received impromptu modifications directly on the battlefield. Crews often added extra DT machine guns to the turret roof for anti-aircraft defense, addressing a critical vulnerability.
The base model’s weight increased over time as units applied additional armor plates to vulnerable areas. These field-applied armor improvements were especially common after encountering enemy anti-tank weapons.
Crews frequently painted identification markings and tactical symbols directly on their tanks. These decals varied by unit and battle conditions, helping coordinate tank formations during complex operations.
Some T-26 tanks were completely repurposed in the field when damaged, with surviving components salvaged to create improvised armored vehicles. Turrets might be removed and the chassis used for transport or as mobile gun platforms based on immediate battlefield needs.
Prototype T-126
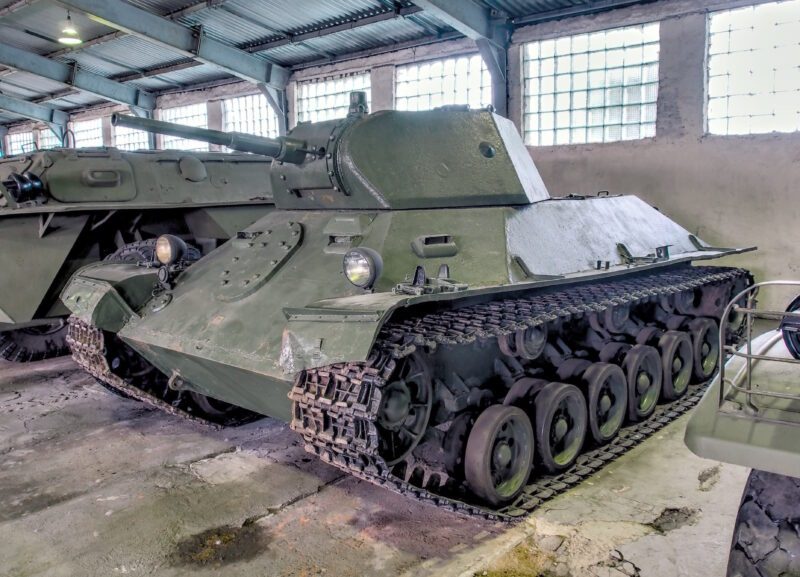

The T-126 was a significant Soviet prototype tank developed in 1940 as part of efforts to replace the aging T-26 light tank. This experimental vehicle was designed by Factory #174’s design bureau and served as an important stepping stone toward the later T-50 light tank.
Weighing approximately 17 tons, the T-126 featured impressive armor protection for its time. The hull had a slightly different shape compared to the T-50, with front armor reaching 55mm thick and side armor at 45mm. This represented a substantial improvement over the T-26’s protection capabilities.
The tank was powered by a V-3 diesel engine generating 250 horsepower, allowing it to reach speeds of 35 km/h with a road range of about 260 km. This provided better mobility than its predecessor.
For armament, the T-126 carried a 45mm 20K cannon with 150 rounds and two 7.62mm machine guns (DT and DS-39 models) with over 4,000 rounds of ammunition. The tank featured both telescopic and panoramic sights for improved targeting.
The four-person crew included a driver, commander, gunner, and radio operator. Despite its promising design, the T-126 experienced numerous small technical issues during factory testing in September 1940, primarily due to its complex construction.
Only one prototype was ever built, which can now be found in the Tank Museum at Kubinka. While the T-126 itself didn’t enter production, it played a crucial role in Soviet tank development, with its design elements influencing the successful T-50 light tank.
The T-126 in War Thunder:
Who does not know the F2P tank and plane war game War Thunder can download it from here for free:
Legacy and Influence
The T-26 tank left a lasting mark on military history as one of the most important Soviet tanks of its era. With over 10,000 units produced, it became the backbone of the Red Army‘s tank force by the time Germany invaded in 1941.
Its combat experience in the Spanish Civil War provided valuable lessons for tank warfare. The T-26 demonstrated the importance of armor protection and firepower balance, influencing tank design philosophy across several nations.
The tank served as a foundation for numerous variants, including self-propelled guns and tank destroyers like the SU-1 and T-26-4. These developments helped shape the evolution of Soviet armored vehicle design throughout World War II.
Despite becoming outdated during the later stages of the war, the T-26’s influence continued through the lessons learned from its strengths and weaknesses. Soviet engineers applied this knowledge to future tank designs.
The T-26 also contributed to Soviet military doctrine, helping commanders understand how light tanks could be effectively deployed in combat operations. This expertise proved crucial during the early defensive battles against German forces.
Today, surviving T-26 tanks can be found in military museums worldwide, serving as reminders of this influential Soviet light tank that helped shape armored warfare in the 20th century.
Frequently Asked Questions
The T-26 tank holds an important place in Soviet military history, with specific design elements and combat experiences that shaped its legacy. Many aspects of this light tank’s development and use continue to interest military historians and enthusiasts.
How did the T-26 perform in World War II engagements?
The T-26 showed mixed performance during World War II. Early in the conflict, it suffered heavy losses against German forces due to its thin armor and mechanical reliability issues.
By 1941, the T-26 was largely obsolete when facing German tanks like the Panzer III and IV. Its 45mm gun remained effective against light armor, but its own protection proved inadequate against most German anti-tank weapons.
The tank performed better in the Soviet-Finnish War where it faced fewer advanced enemy tanks. Still, difficult terrain and maintenance problems limited its effectiveness even there.
What were the main variants of the T-26 and their differences?
The T-26 underwent numerous modifications throughout its production run. The initial T-26 Model 1931 featured twin turrets with machine guns, based closely on the Vickers design.
The Model 1933 introduced a single turret with a 45mm gun, significantly improving firepower. This became the most produced variant.
Specialized versions included flamethrower tanks (OT-26, OT-130), command tanks with enhanced radio equipment, and artillery support variants. The T-26RT featured improved radio communication systems for coordinating units in battle.
Engineer variants were also developed for bridge-laying and mine-clearing operations, showing the platform’s versatility.
How does the T-26 compare to its contemporaries, like the Pershing or the T26E5?
The T-26 shouldn’t be compared directly with the American Pershing or T26E5, as these were heavy tanks from a later generation. The Soviet T-26 was a light tank from the early 1930s, while the Pershing entered service near the end of WWII.
A more appropriate comparison would be with contemporary light tanks like the German Panzer I and II or the Japanese Type 95 Ha-Go. Against these, the T-26’s 45mm gun provided superior firepower for its time.
The T-26 offered good mobility but featured thinner armor than many of its later contemporaries. Its simple design allowed for mass production, which was a key Soviet strategy.
Can you describe the historical significance of the T-26 in Soviet military strategy?
The T-26 represented the backbone of Soviet armor forces throughout the 1930s. It aligned with Soviet deep battle doctrine, which emphasized breakthrough operations and exploitation of weak points.
Soviet military planners valued the T-26 for its ability to support infantry advances and engage enemy positions directly. Over 11,000 were produced, making it the most numerous tank in the Red Army before WWII.
The tank saw action in the Spanish Civil War, providing valuable combat experience for Soviet crews and technical teams. Lessons learned from these deployments influenced later Soviet tank designs.
The T-26’s limitations revealed during early WWII engagements accelerated Soviet tank development, leading to more advanced designs like the T-34.
What advancements did the T-26 introduce into tank design?
While based on the British Vickers design, the T-26 featured Soviet modifications that improved upon the original. The transition from twin turrets to a single turret with a 45mm gun represented an important evolution in firepower.
The tank incorporated welded armor in later versions, moving away from riveted construction that created dangerous secondary projectiles when hit. This manufacturing technique would become standard in later tanks.
The T-26 served as a platform for testing various auxiliary equipment and specialized roles, contributing to Soviet understanding of combined arms operations. Its design influenced some aspects of later Soviet light tanks.
How has the T-26 been represented in media and video games such as War Thunder?
The T-26 appears in several historical combat games, including War Thunder where it’s positioned as an early-tier Soviet light tank. Its in-game characteristics generally reflect its historical strengths and weaknesses.
World of Tanks features the T-26 as a tier 2 light tank, highlighting its mobility but limited protection. The game includes several of its historical variants.
Military documentaries often feature the T-26 when discussing early Soviet armor or the Spanish Civil War. Historical reenactments sometimes include restored or replica T-26 tanks, preserving its visual legacy.
Several scale model companies produce detailed T-26 kits for enthusiasts, showcasing the various modifications and camouflage patterns used throughout its service life.
References and literature
Krieg der Panzer (Piekalkiewicz)
Soviet Tanks and Combat Vehicles of World War Two (Steven J. Zaloga, James Grandsen)
Panzer und andere Kampffahrzeuge von 1916 bis heute (Christopher F. Foss, John F. Milsom, Colonel John Stafford Weeks, Captain Georffrey Tillotson, Richard M. Ogorkiewicz)
The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II (Chris Bishop)
Operation Barbarossa: the Complete Organisational and Statistical Analysis, and Military Simulation, Volume I – IIIB (Nigel Askey)








You did a great job well done. It is the site I was looking for to be able to do my missions on the 2WW with the Arma3 tactical simulator.