British three-seat light bomber, heavy fighter and night fighter Bristol Blenheim.
History, development, service, specifications, statistics, pictures and 3D model.

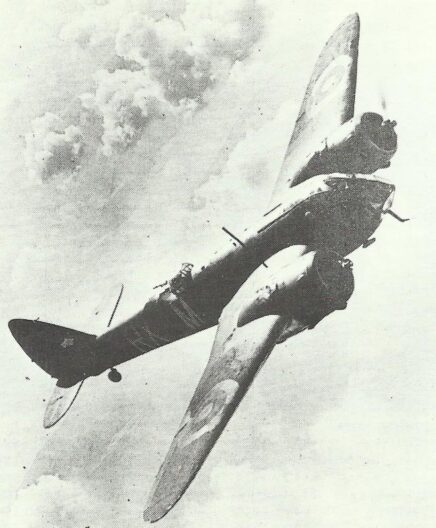
Bristol Type 142 Blenheim
Type: Light bomber, heavy fighter night fighter.
History:
Table of Contents
It had been that papers tycoon Lord Rothermere that requested the Bristol corporation to develop him a rapid business plane to transport a pilot and 6 persons at 240 mph (ca. 386 km/h), considerably quicker than any kind of Royal Air Force single-seat fighter plane at this time.
The outcome had been the Type 142, the original innovative stressed-skin monoplane in the UK together with retractable landing gear, flaps and, following a hold out, imported US variable-pitch propellers. Its performance staggered including the developer, Mr Barnwell.
For on Air Ministry try it achieved 307 mph (ca. 494 km/h). The expected outcome was the Blenheim bomber, to build which Barnwell developed a fresh fuselage together with mid-wing as well as bomb bay under it. Pilot and navigator/bomb-aimer seated within the tidy glazed nose, as well as a part-retractable dorsal turret had been included behind the wing.
The Blenheim I was purchased in what were enormous numbers to a corporation practically lacking employment. Finally, 1,134 had been constructed, several of which executed gallant bombing raids at the beginning of the war as well as were then reconstructed as IF fighter layout (several getting the AI Mk III, the very first functional fighter radar on the globe).
The quick, fresh bomber fired up extraordinary international attention and several had been exported to Finland, Turkey, Yugoslavia, Lithuania, Romania and Greece.
To supply a navigator/bomb-aimer place in front of the pilot the nose was then extended 3ft (0.91 m) and this model had been christened Bolingbroke, a brand preserved for the amount of Blenheims constructed in Canada (the Bolingbroke Mk III becoming a twin-float seaplane).
A modified asymmetric nose was developed for manufacturing in the fast Mk IV, which afterwards got a fighter machine-gun group (IVF) or a manual rear-firing chin gun (IVL). Ultimately having a two-gun chin turret.
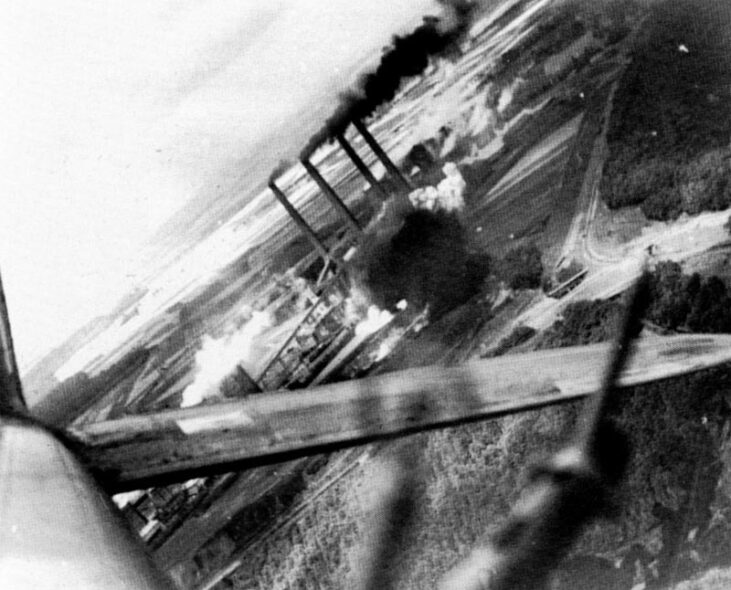
Produced by Bristol, Avro and Rootes, like the Mk I, the IV had been the primary battle model with the RAF, 3,297 being supplied and executing a lot of daylight missions in several theaters of war.
The heavily armed and armored two-seat Bisley strike aircraft failed to enter manufacturing, however the three-seat comparable did, as the Blenheim Mk V. Weighty and under powered, the 902 VDs worked in North Africa and Asia.
Users: Canada, Finland, France, Greece, Yugoslavia, Lithuania, Portugal, Romania, Turkey, UK (RAF).
Pictures Bristol Blenheim
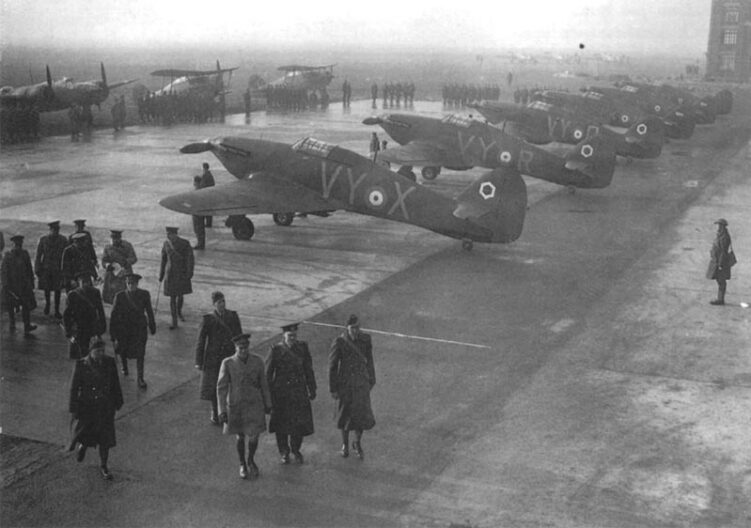
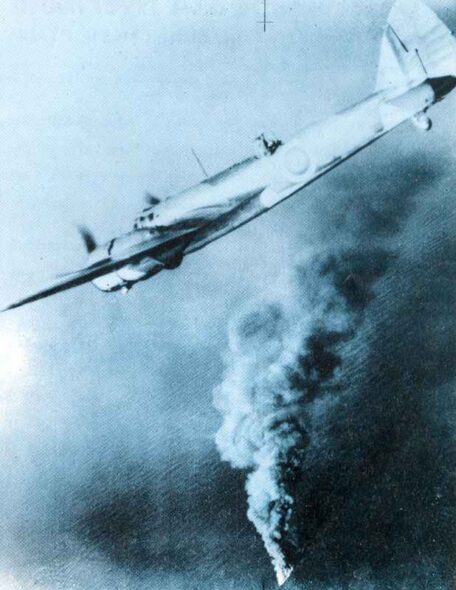


Specifications Bristol Blenheim
Specifications:
Specification | Blenheim I | Bolingbroke | Blenheim IVL | Blenheim V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Type | Light bomber | |||
Power Plant | 2 x 840 hp Bristol Mercury VII | 2 x 840 hp Bristol Mercury VII (IV: 2 x 750-920 hp Twin Wasp Junior, Cyclone or Mercury XX) | 2 x 920 hp Mercury XV | 2 x 950 hp Mercury XXX |
Accommodation | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
Wing span | 56ft 4in (17.17m) | 56ft 4in (17.17m) | 56ft 4in (17.17m) | 56ft 1in (17.31m) |
Length overall | 39ft 9in (12.11m) | III: 46ft 3in (14.10m) | 42ft 9in (13.0m) | 43ft 11 in (13.38 m) |
Height overall | 12ft 10in (3.91m) | III: 18ft (5.49m) | 12ft 10in (3.91m) | 12ft 10in (3.91m) |
Weight empty | 8,700lb (3,946kg) | 8,700lb (3,946kg) | 9,790lb (4,441kg) | 11,000lb (4,990 kg) |
Weight loaded | 12,250lb (5,557kg) | 13,400lb (6,078kg) | 14,400lb (6,531kg) | 17,000lb(7,711 kg) |
Maximum speed | 285mph( 459km/hr) | 245-260mph (394-419km/hr) | 266mph; early VIs: 295mph (428km/hr/475km/hr) | 245-260mph (394-419km/hr) |
Initial climb | 1,500ft (457m)/min | 1,500ft (457m)/min | 1,500ft (457m)/min | 1,500ft (457m)/min |
Service ceiling | 31,500ft (9,600m) | III: 26,000ft(7,925m) | 31,500ft (9,600m) | 31,500ft (9,600m) |
Range | 1,125 miles (1,811km) | 1,800 miles (2,898 km) | 1,950 miles (3,138km) | 1,600 miles (2,576km) |
Armament:
Model | Specification |
|---|---|
Blenheim I | 1 x 0.303in fixed in nose, 1 x 0.303in Vickers K in dorsal turret |
Blenheim IVL | 1 x 0.303in Vickers in nose, 2 x 0.303in Brownings in chin turret, 2 x 0.303in Brownings in dorsal turret |
Blenheim IF, IVF (fighter) | 4 x fixed 0.303in Brownings under fuselage extra, no bombs |
Bomb load | 1,000 lb (454kg) internal; non-standard aircraft had underwing racks for 2 x 250lb (225kg) bombs |
Service statistics:
Bristol Blenheim | figures |
|---|---|
First flight | 25 June 1936 (Blenheim I) |
Service delivery | November 1936 |
Final delivery | June 1943 (VD) |
Price per unit | unknown |
Production figures | 5,213 + c.120 seaplanes (1,134 Is; 3,297 Bolingbroke and IVs, 902 Vs) |
References and literature
Luftkrieg (Piekalkiewicz)
Das große Buch der Luftkämpfe (Ian Parsons)
Technik und Einsatz der Kampfflugzeuge vom 1. Weltkrieg bis heute (Ian Parsons)
Combat Aircraft of World War II (Bill Gunston)