German Orders of Battle for the Battle of France of June 8, 1940.
The offensive started after Dunkirk Evacuation on June 5 with the attack of Army Group B.

Battle of France
Table of Contents
The Battle of France, also known as the Fall of France, was a major military campaign that took place in May and June of 1940 during World War II.
Overview
Timeline: The battle began on May 10, 1940, and ended with the French surrender on June 22, 1940.
Combatants: Nazi Germany and its allies invaded France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands. The defending forces included France, Britain, Belgium, and the Netherlands.
German strategy: The Germans employed a tactic called ‘Blitzkrieg‘ (lightning war), which involved rapid, coordinated attacks using tanks, aircraft, and motorized infantry.
Invasion route: The main German thrust came through the Ardennes forest, which was thought to be impassable for tanks, catching the Allies off guard.
Allied response: The Allies were unprepared for the speed and effectiveness of the German assault, leading to confusion and disorganization.
Dunkirk evacuation: From May 26 to June 4, over 338,000 Allied troops were evacuated from the beaches of Dunkirk to England.
Paris falls: The Germans captured Paris on June 14, 1940.
Armistice: France signed an armistice with Germany on June 22, 1940, effectively surrendering.
Consequences: France was divided into occupied and unoccupied zones, with the Vichy regime governing the latter. Britain stood alone against Nazi Germany in Western Europe.
Military impact: The rapid defeat of France shocked the world and established Nazi Germany as the dominant power in continental Europe.
The Battle of France was a decisive German victory that dramatically altered the course of World War II and had far-reaching consequences for Europe and the world.
Battle of Dunkirk
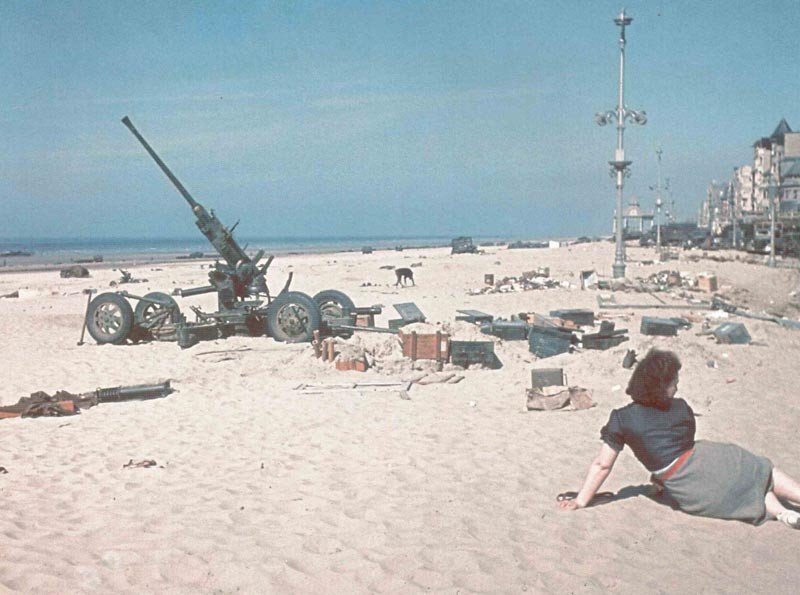

The Battle of Dunkirk (May 26-June 4, 1940) was a significant event during World War II where Allied forces were evacuated from the beaches of Dunkirk, France, in Operation Dynamo.
Background:
– German forces had advanced rapidly through France, trapping Allied troops against the English Channel
– Around 400,000 British and French troops were cornered in the Dunkirk pocket
The Evacuation:
– Operation Dynamo involved both military and civilian vessels
– The “Little Ships of Dunkirk” – hundreds of civilian boats assisted in the rescue
– Royal Navy vessels and RAF provided protection during the evacuation
– Around 338,000 troops were successfully evacuated
– British forces: 198,000
– French forces: 140,000
Significance:
– Prevented complete destruction of British Expeditionary Force (BEF)
– Saved a significant portion of France’s best troops
– Boosted British morale (“Dunkirk Spirit”)
– Allowed Britain to continue fighting
– Churchill’s famous “We shall fight on the beaches” speech
Challenges:
– Constant German air attacks
– Shallow waters prevented larger ships from approaching the beach
– Limited port facilities due to German bombing
– Troops had to wait in long lines while exposed to enemy fire
Aftermath:
– Most military equipment was left behind
– France fell to Germany shortly after
– Britain avoided a potentially catastrophic military defeat
– Became a symbol of British resilience and determination
The evacuation was considered a “miracle” given the circumstances, and played a crucial role in Britain’s ability to continue fighting in World War II.
German Orders of Battle during the Battle of France
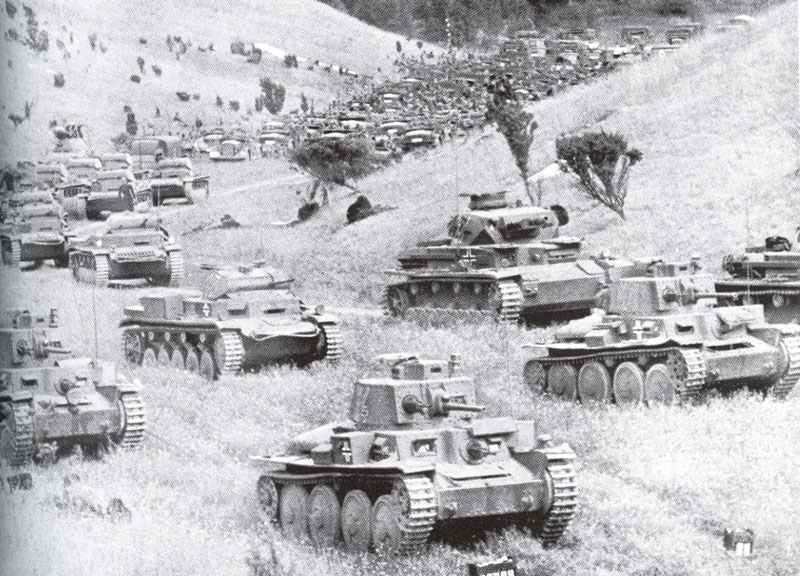

From 9 April (when German troops invaded Denmark and Norway) to the armistice with France on 25 June, the German Army confirmed the superiority of its organization and tactics. Losses in Norway were 5,636 men; the invasion of France and the Low Countries cost 27,074 killed, 111,034 wounded and 18,348 missing. On some single days in World War One the losses were higher.
Schematic layout of the German Wehrmacht from June 8th, 1940
Schematic layout:
Army Group | Army | Corps | Divisions |
|---|---|---|---|
Army Group B located in northern France at the Channel Coast (Reserves: 1, 11, 19, 30, 8, 28, 217 Infantry divisions) | 4 Army | II Corps | 11 Fast Brigade , 12, 57, 32, 31 Infantry Divisions |
XXXVIII Corps | 6, 46, 27 Infantry, 1 Cavalry division |
||
XV Corps | 5, 7 Panzer, 2 motorized Infantry division |
||
6 Army | XXXX Corps | 87, 44 Infantry division |
|
V Corps | 62, 263 Infantry, parts 94 Infantry division |
||
XXXXIV Corps | 72 Infantry, 1 Mountain, parts 98., parts 83. Infantry division" |
||
9 Army (Reserves: parts 88, 96 Infantry division) | XVIII Corps | 25, 290 Infantry, parts 81 Infantry Division |
|
XXXXII Corps | 292, 50, 291 Infantry Division |
||
Panzer Group Kleist | XIV Corps | 9, 10 Panzer, 9 Infantry, 13 motorized Infantry division, Infantry Regiment Grossdeutschland (motorized) |
|
XVI Corps | 3, 4 Panzer division, 4., 33 Infantry, 1., 2 SS-divisions (motorized) |
||
Army Group A located in Northeast France (Reserves: 7, 211, 253, 267, 269 Infantry division) | 2 Army | VI Corps | 5, 293, 15, 205 Infantry division |
XXVI Corps | 45, 34 Infantry division |
||
IX Corps | 294, 295 Infantry division |
||
12 Army (Reserves: 298 Infantry division) | III Corps | 3, 23, 52 Infantry division |
|
XIII Corps | 17, 21, 260 Infantry division |
||
XXIII Corps | 73, 86, 82 Infantry division |
||
XVII Corps | 10, 26 Infantry, SS-Police division |
||
Panzer Group Guderian | XXXIX Corps | 1, 2 Panzer, 29 motorized Infantry division |
|
XXXXI Corps | 6, 8 Panzer, 20 motorized Infantry division |
||
16 Army (Reserves: 16, 76, 68, 212 Infantry division) | VII Corps | 24, 299, 36, 58 Infantry division |
|
XXXVI Corps | 71, 169 Infantry division |
||
XXXI Corps | 183, 161, 162 Infantry division |
||
Army Group C in the Saar and Rhine front in Southwest Germany | 1 Army (Reserves: 79, 168, 197, 198 Infantry division) | XXXXV Corps | 167 Infantry, parts 96 Infantry division |
XXX Corps | 258 Infantry, parts 93 Infantry division |
||
XII Corps | 75, 268 Infantry division |
||
XXIV Corps | 60, 252 Infantry division |
||
XXXVII Corps | 257, 262, 215, 246 Infantry division |
||
7 Army (Reserves: 213, 218, 221, 239 Infantry division) | XXV Corps | 557, 555 Infantry division |
|
XXXIII Corps | 554, 556 Infantry division |
||
subordinated to OKW (Headquarter of the Wehrmacht), located in Poland and Norway | 18 Army (Poland, Reserves: 216, 227, 251 Infantry division) | X Corps | 208, 225, 254 Infantry division |
AOK Norwegen (HQ Norway) | XXI Corps | 2, 3 Mountain, 69, 214, 163, 181, 196 Infantry division |
|
OKH Reserves | Group West | XXVIII Corps | 14, 18, 56, 61, 223, 255, 256 Infantry division, 3 SS-Infantry division Totenkopf (motorized) |
Group East | XXIX Corps | 207, 297, 78, 170, 296, 35, 206 Infantry division; in transfer: 22, 164 Infantry division |
|
in Germany | 228, 231, 311 Infantry division |
||
Oberost (East Prussia) | XXXIV, XXXV Corps | 209, 365, 372, 379, 393 Infantry division |
|
Reserve Army and Commander of the army armament | XXXII Corps | 351, 358, 386, 395, 399 Infantry division |
Overview of fully established and operational divisions of the Wehrmacht, Waffen-SS and Luftwaffe on June 8, 1940
Overview:
| Panzer | mot.Inf. | Cav. | Inf. | Mountain | Airborne | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Army Group B | 6 | 5 | 1 | 27 | 1 | - | 40 |
| Army Group A | 4 | 2 | - | 39 | - | - | 45 |
| Army Group C | - | - | - | 23 | - | - | 23 |
| Norway | - | - | - | 5 | 2 | - | 7 |
| Poland, East Prussia | - | - | - | 11 | - | - | 11 |
| Reserves | - | 1 | - | 24 | - | 2 | 27 |
| TOTAL | 10 | 8 | 1 | 129 | 3 | 2 | 153 |
Approximate organization strength of the major types of the German Army divisions in 1939-1940:
| Infantry Division | motorized Infantry Division (1939) | Mountain Division | Panzer Division (1939-40) | Light Division | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units total | 87 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| Officers | 500 | = | ? | 400 | 400 |
| Officials | 100 | = | ? | 100 | 100 |
| NCOs | 2,500 | = | ? | 2,000 | 1,600 |
| Privates | 13,400 | = | ? | 9,300 | 8,700 |
| Total men | 16,500-17,200 (35 divisions of 1st wave 18,000 | 16,500 | 13,056 | 11,800 | 10,800 |
| Infantry Regiments | 3 with 3,000 men each | = | 2 with 3,000 men each | 2 with 3,000 men each | 1 or 2 with 2,000 or 3,000 men each |
| Machine guns MG34 | 643 (116 heavy) | = | 569 | 220 | 460 |
| Anti-tank rifles | 90 | = | - | ||
| Mortars | 142 (84 x 5cm, 58 x 8.1cm) | = | 118 (60 x 8.1cm, 58 x 5cm) | 50 | 60 |
| Infantry guns | 24 (6 x 15cm, 18 x 7.5cm) | = | 4 (15cm) | 10 | 10 |
| Anti-tank guns | 75 (3.7cm Pak 36) | = | 51 (45 x 3.7 cm, 6 x 4.7cm) | 50 | 50 |
| Howitzers and guns | 48 (8 x 15cm, 36 x 10.5cm leFH, 4 x 10.5cm guns) | = | 36 (8 x 15cm, 12 x 10.5cm, 16 x 7.5cm) | 28 | 24 (10.5cm leFH) |
| Anti-aircraft guns (2cm) | 11 | = | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Armored Cars | 3 | 30 | - | 100 | 100 |
| Tanks | - | - | - | 324 | 86 |
| Trucks | 500 | 1,700 | - | 1,400 | 1,400 |
| Cars | 400 | 1,000 | - | 560 | 600 |
| Motorcycles | 452 | 1,300 | - | 1,300 | 1,100 |
| Sidecars | 200 | 600 | - | 700 | 600 |
| Horses | 5,375 | - | ? | - | - |
| Horse-drawn carriages | 1,133 | - | ? | - | - |
More about: Germany Army Unit Organization 1939-41.
References and literature
World War II – A Statistical Survey (John Ellis)
Der Grosse Atlas zum II. Weltkrieg (Peter Young)
Kriegstagebuch des Oberkommandos der Wehrmacht, Band 1-8 (Percy E. Schramm)
Kraftfahrzeuge und Panzer der Reichswehr, Wehrmacht und Bundeswehr (Werner Oswald)
The Armed Forces of World War II (Andrew Mollo)